[ad_1]
Many of the businesses promising “net-zero” emissions to guard the local weather are counting on huge swaths of forests and what are referred to as carbon offsets to satisfy that objective.
On paper, carbon offsets seem to steadiness out an organization’s carbon emissions: The firm pays to guard timber, which take up carbon dioxide from the air. The firm can then declare the absorbed carbon dioxide as an offset that reduces its internet influence on the local weather.
However, our new satellite tv for pc evaluation reveals what researchers have suspected for years: Forest offsets won’t really be doing a lot for the local weather.
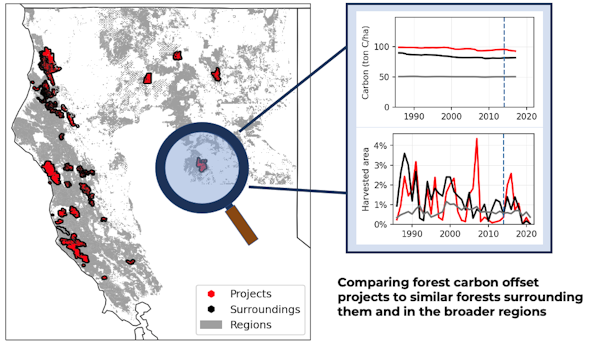
When we checked out satellite tv for pc monitoring of carbon ranges and logging exercise in California forests, we discovered that carbon isn’t rising within the state’s 37 offset venture websites any greater than in different areas, and timber firms aren’t logging lower than they did earlier than.
The findings ship a fairly grim message about efforts to manage local weather change, and so they add to a rising checklist of considerations about forest offsets. Studies have already proven that initiatives are usually overcredited in the beginning and won’t final so long as anticipated. In this case we’re discovering a much bigger subject: a scarcity of actual local weather profit over the ten years of this system to date.
But we additionally see methods to repair the issue.
How forest carbon offsets work
Forest carbon offsets work like this: Trees seize carbon dioxide from the air and use it to construct mass, successfully locking the carbon away of their wooden for the lifetime of the tree.
In California, landowners can obtain carbon credit for retaining carbon shares above a minimal required “baseline” stage. Third-party verifiers assist the landowners take stock by manually measuring a pattern of timber. So far, this course of has solely concerned measuring carbon ranges relative to baseline and has not leveraged the rising satellite tv for pc applied sciences that we explored.
Forest homeowners can then promote the carbon credit to personal firms, with the concept they’ve protected timber that will in any other case be reduce down. These embody giant oil and gasoline firms that use offsets to satisfy as much as 8% of their state-mandated reductions in emissions.
Forest offsets and different “natural climate solutions” have obtained an excessive amount of consideration from companies, governments and nonprofits, together with throughout the U.N. local weather convention in November 2022. California has one of many world’s largest carbon offset applications, with tens of tens of millions of {dollars} flowing by way of offset initiatives, and is commonly a mannequin for different nations which might be planning new offset applications.
It’s clear that offsets are enjoying a big and rising position in local weather coverage, from the person to the worldwide stage. In our view, they must be backed by one of the best out there science.
3 potential issues
Our research used satellite tv for pc information to trace carbon ranges, tree harvesting charges and tree species in forest offset initiatives in contrast with different comparable forests in California.
Satellites provide a extra full report than on-the-ground stories collected at offset initiatives. That allowed us to evaluate all of California since 1986.
Adapted from Coffield et al., 2022, Global Change Biology
From this broad view, we identified three issues indicating a scarcity of local weather profit:
• Carbon isn’t being added to those initiatives quicker than earlier than the initiatives started or quicker than in non-offset areas.
• Many of the initiatives are owned and operated by giant timber firms, which handle to satisfy necessities for offset credit by retaining carbon above the minimal baseline stage. However, these lands have been closely harvested and proceed to be harvested.
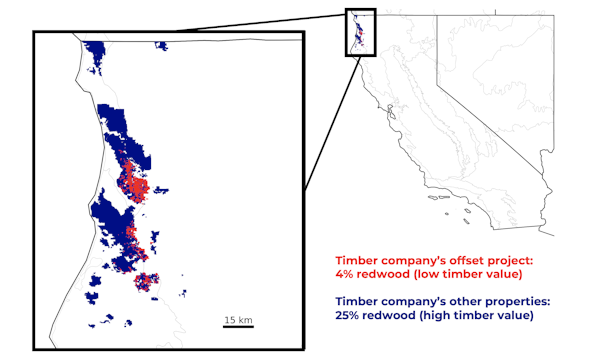
• In some areas, initiatives are being placed on lands with lower-value tree species that aren’t in danger from logging. For instance, at one giant timber firm within the redwood forests of northwestern California, the offset venture is barely 4% redwood, in contrast with 25% redwood on the remainder of the corporate’s property. Instead, the offset venture’s space is overgrown with tanoak, which isn’t marketable timber and doesn’t must be protected against logging.
Adapted from Coffield et al., 2022, Global Change Biology, CC BY-ND
How California can repair its offset program
Our analysis factors to a set of suggestions for California to enhance its offsets protocols.
One suggestion is to start utilizing satellite tv for pc information to watch forests and make sure that they’re certainly being managed to guard or retailer extra carbon. For instance, it may assist foresters create extra real looking baselines to check offsets in opposition to. Publicly out there satellite information is bettering and might help make carbon offsetting extra clear and dependable.
California may also keep away from placing offset initiatives on lands which might be already being conserved. We discovered a number of initiatives owned by conservation teams on land that already had low harvest charges.
Additionally, California may enhance its offset contract protocols to ensure landowners can’t withdraw from an offset program sooner or later and reduce down these timber. Currently there’s a penalty for doing so, nevertheless it won’t be excessive sufficient. Landowners could possibly start a venture, obtain an enormous revenue from the preliminary credit, reduce down the timber in 20 to 30 years, pay again their credit plus penalty, and nonetheless come out forward if inflation exceeds the legal responsibility.
Ironically, whereas supposed to assist mitigate local weather change, forest offsets are additionally susceptible to it – significantly in wildfire-prone California. Research suggests that California is vastly underestimating the local weather dangers to forest offset initiatives within the state.
The state protocol requires solely 2% or 4% of carbon credit be put aside in an insurance pool in opposition to wildfires, although a number of initiatives have been broken by current fires. When wildfires happen, the misplaced carbon might be accounted for by the insurance coverage pool. However, the pool might quickly be depleted as yearly burned space will increase in a warming local weather. The insurance coverage pool have to be giant sufficient to cowl the worsening droughts, wildfires and illness and beetle infestations.
Considering our findings across the challenges of forest carbon offsets, specializing in different choices, akin to investing in photo voltaic and electrification initiatives in low-income city areas, might present less expensive, dependable and simply outcomes.
Without enhancements to the present system, we could also be underestimating our internet emissions, contributing to the income of huge emitters and landowners and distracting from the true options of transitioning to a clean-energy economic system.
This article is republished from The Conversation below a Creative Commons license. Read the unique article. Top picture: Andy Dutton/Unsplash
[ad_2]



